The challenge of poor-quality products continues to threaten growth as more consumers embrace off-grid solutions. A 2017 Lighting Global study assessed 17 of the top-selling non-quality verified products in five markets. The study found that 94% of the solar products did not meet the Lighting Global Quality Standards due to lack of warranty, false advertising, and lack of product and battery durability. The prevalence of these low-quality products is a lose-lose for the markets as distributors of quality products lose market share and consumers end up paying more in the long-run through repeat purchases.
The adoption of standards is a critical first step towards elimination of poor-quality products in the market. ACE TAF together with IFC are supporting the adoption of the International Electrochemical Commission (IEC) 62257-9-5 and 62257-9-8 standards for solar powered equipment under 350w in all ACE TAF countries. The purpose of these standards is to ensure consumers get value from their investment by defining a clear and transparent baseline level of quality and durability and to guard against false advertising, especially on the capacity of the battery and lighting hours. To date, Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria and Zambia have adopted the standards. Sierra Leone, Senegal, Zimbabwe, Uganda, Tanzania and Ethiopia are in the advanced consultation phase. Malawi and Mozambique are in a preparatory phase.
However, adoption of the standards is only a first step towards consumer protection. A structured and well planned follow up is required to ensure the standards are consistently implemented and enforced so that the share of low-quality products in any country reduces significantly. The figure below outlines the process for successful standards adoption and enforcement.
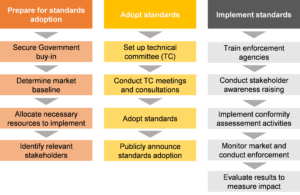
The standards adoption process
In countries where we have successfully supported the standards adoption, we have started the next steps towards enforcement. Two examples are found in Nigeria and Zambia.
In Nigeria, the Standards Organisation of Nigeria (SON) adopted the IEC standards quality standards as the mandatory national standards in June 2020. Since the adoption, ACE TAF has worked with SON to set a Quality Assurance Market Surveillance and Enforcement Plan to guide implementation. Most importantly, the Plan maps out resource needs at each stage so that SON can effectively plan with donor partners. A quality testing laboratory is being set up to support market surveillance activities.
In Zambia, the Zambia Bureau of Standards (ZABS) and Energy Regulation Board (ERB) adopted the IEC quality standards in January 2021. The adoption process identified the need to link quality standards to fiscal incentives to reduce the presence of poor-quality products in the market. ACE TAF is now working with the Ministry of Energy, ERB, ZABS and others to ensure the linkage is an integral part of the importation process.
Read more: Standards for Stand-Alone Solar – Guidance for Governments